Electromagnetic Motors
Without electric motors
(more correctly electromagnetic), our modern life would look much different. The physics of these motors is fascinating. All of them are based on the effect of the magnetic part of the Lorentz force: If an electric charge moves through a magnetic field, it feels a force which is proportional to the cross-product of its velocity vector and the magnetic field vector. The above animation shows the principle of a simple direct-current motor
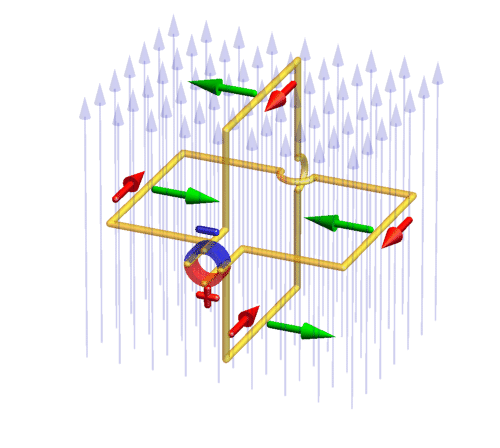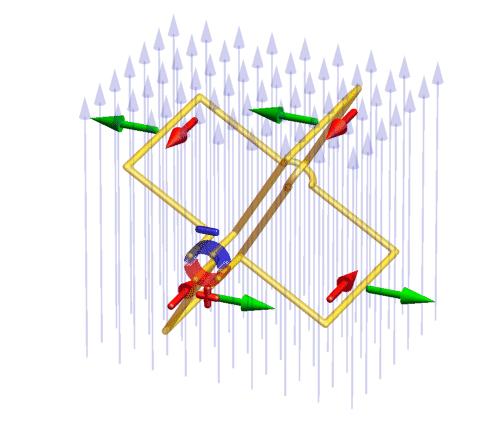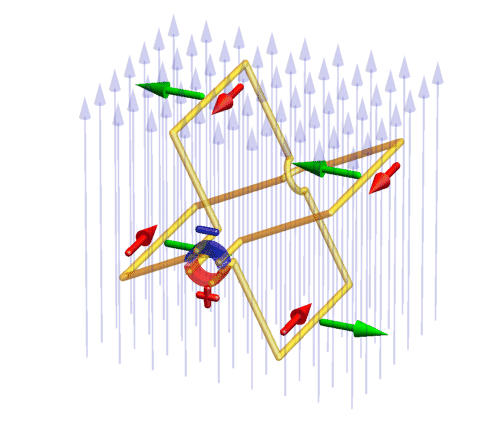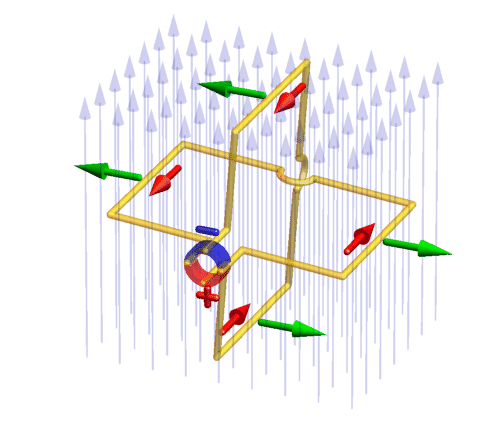
with commutator
(red/blue ring): a conducting rotating wire frame (yellow) is hung within a constant magnetic field (vertical light blue arrows) and connected with a commutator. On the commutator, a constant voltage is applied which drives electric currents (red) through the wires. The commutator makes sure that the current direction switches in such a way that the Lorentz force (green) acting on the currents drives the frame rotation always into the same direction.

An induction motor
is an ingenious construction that uses two fundamental effects: The Lorentz force (see also left panel), and Faraday's electromagnetic induction. As the animation shows, an electrically conducting wire frame (yellow) is placed into a rotating magnetic field (light blue arrows), which induces currents (red) in the frame, on which the same magnetic field exerts a Lorentz force (green). If the rotation speed between frame and field would be the same, both induction and Lorentz force would vanish. Thus, the frame rotation is always slower than the field rotation and adjusts itself in such a way that the generated momentum balances the external mechanical load! Moreover, in contrast to the DC motor in the left panel, no external voltage is required for generating the currents in the wire frame.
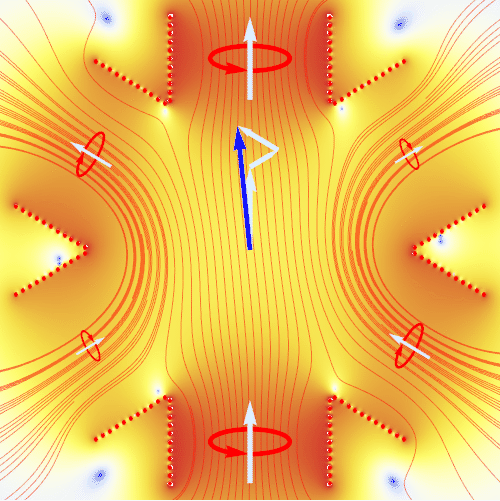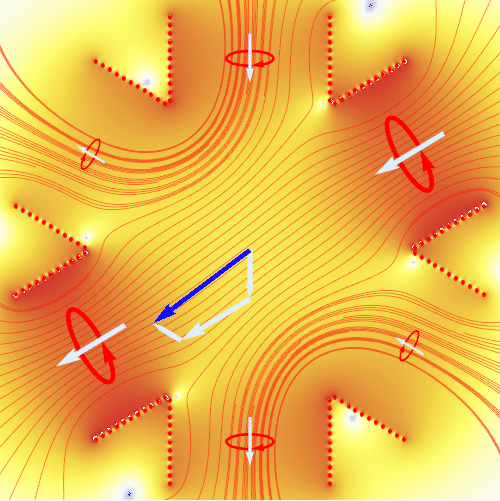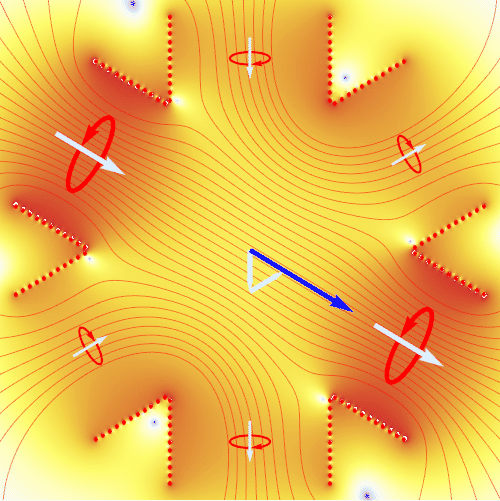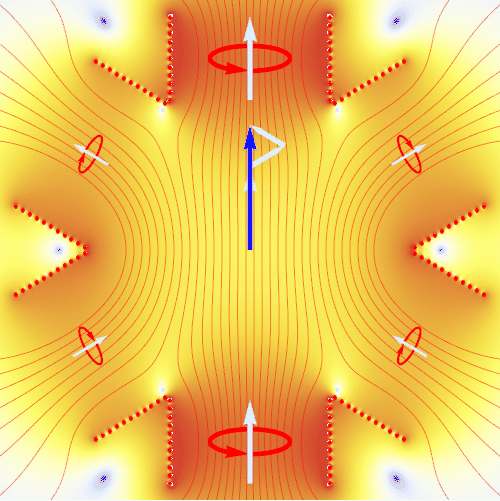
An induction motor requires the application of a rotating magnetic field. The animation here shows how this is realized by using three pairs of electromagnets at 120° angle to each other. By applying alternating currents (red circles) to these magnets with a mutual phase shift of 120°, one generates at the center an uniformly rotating magnetic field (blue arrow) with constant amplitude. The animation shows the result of an exact numerical calculation. The coloring visualizes the magnetic field strength (from blue to red), and red lines are magnetic field lines.
For more details about all these topics, please see my lecture on Electricity & Magnetism which you can find on this web page.